US Congress passes $1 trillion infrastructure bill; Spending bill tax credits could hike solar installs by 44%
Our pick of the solar news you need to know.

Related Articles
US Congress passes bill to upgrade power grid for wind, solar
The U.S. Congress passed November 6 President Biden's $1 trillion infrastructure bill that includes $65 billion of investments in the power grid to accommodate rising renewable energy capacity and demonstration cleantech projects.
The Bipartisan Infrastructure Deal authorises spending on road, rail, broadband, water and electricity networks in the largest upgrade of US infrastructure in a generation. Approved by the Senate in August, the House of Representatives backed the bill 228 votes to 206.
The bill will fund thousands of miles of new transmission lines for wind and solar projects and a new Grid Deployment Authority within the Department of Energy (DOE) that will fast-track transmission build along roads and railways. Spending will also be allocated to advanced transmission solutions and smart grids as well as demonstration nuclear reactor, carbon capture and green hydrogen plants.
President Biden has pledged to fully decarbonise the power sector by 2035, requiring a rapid acceleration in renewable energy deployment and an expansion and modernisation of the power grid. Falling solar and wind costs have spurred development but a lack of transmission infrastructure and long approval processes are delaying projects.
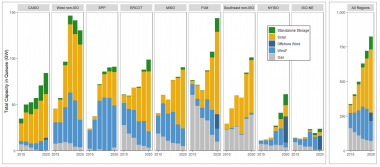
US power generation in interconnection queues
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: Berkeley Lab, May 2021
The bill also allocates $7.5 billion to build the first national network of electric vehicle chargers to accelerate the switch away from fossil fuels.
The Biden Administration is also looking to pass a larger $1.75 trillion social and climate spending bill in the coming weeks. The Build Back Better package sets aside $555 billion for climate measures including an extension of tax credits for solar and wind projects and new tax credits for renewable energy components manufactured in the US.
The US House of Representatives could vote on the larger bill next week, White House economic adviser Brian Deese said November 8. The bill must also pass the narrowly divided Senate, where the Democrats and Republicans both hold 50 seats and Vice President Kamala Harris can wield a tiebreaker vote.
Biden's tax credit extension could hike solar installs by 44%
The 10-year extension of solar investment tax credits proposed in President Biden's $1.75 trillion social and climate spending bill would hike solar installations by 44% over the next decade, research group Wood Mackenzie said in a note November 1.
The extension proposed in the Build Back Better bill would lead to 432 GW of new solar capacity installed by 2030, compared with 300 GW in Wood Mackenzie's base case outlook, it said.
Short-term growth would be limited by current supply chain issues and grid constraints, the research group said. Annual growth in installations would accelerate from 30% in 2025 to 92% by 2030, it said.
"Grid interconnection is already one of the biggest pain points for the industry," Sylvia Leyva Martinez, senior analyst at Wood Mackenzie, said. "While there are additional incentives for grid modernization and transmission capacity in both the infrastructure bill and the [Build Back Better] package, these projects take years to complete."
The tax credit extension would not be enough to meet President Biden's target of a fully decarbonised power grid by 2035, Wood Mackenzie noted.
The US must attain 714 GW of installed solar capacity by 2030 to meet the President's goal, the Department of Energy (DOE) said recently, compared with 528 GW projected by Wood Mackenzie following the tax credit extensions.
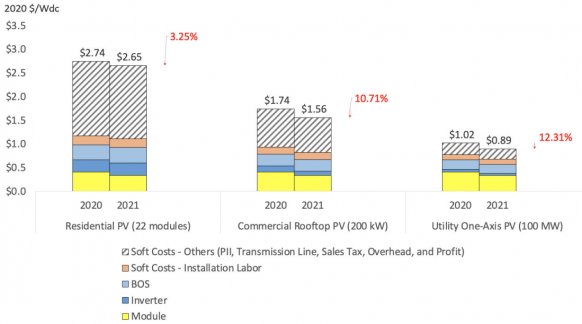
US utility-scale PV costs fell 12% in 2020
US utility-scale PV costs fell by 12% year-on-year to $0.89/Watt in Q1 2021 as lower module prices and better designs were offset by rising raw materials costs, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) said in its latest annual U.S. Solar Photovoltaic System Cost Benchmark report. Since then, the cost of materials and transport has soared following the economic rebound from Covid-19 restrictions.
US benchmark installed PV costs
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: National Renewable Energy Laboratory, November 2021
Despite rising costs, US solar installations in the second quarter rose 45% on a year ago to 5.7 GW as developers chased initial tax credit deadlines, the Solar Energy Industry Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie said in their latest quarterly report.
Developers installed a record 4.2 GW of utility-scale capacity in the second quarter, despite higher commodity prices and supply chain disruption, the report said. Average system prices for fixed-tilt and single-axis tracking projects hiked by 12.5% and 11.6% quarter on quarter, it said.
NREL's modelled benchmark cost represents a 100 MW single-axis tracker plant and is calculated in a bottom-up approach that uses prices paid by developers and installers.
The average cost of a 100 MW PV plant with 60 MW/240 MWh of battery storage also fell by 12% in 2020 to $167/kWh, NREL said.
EU solar employment set to double if renewables target met
Solar industry employment in the European Union (EU) will double to 742,000 by 2030 if the European Commission (EC) meets its target of 40% of power generation from renewables, industry association SolarPower Europe said in its latest annual jobs report.
SolarPower Europe called for the EC to adopt a higher target of 45% of power from renewable energy by 2030 and projected this would increase solar employment to 1.1 million jobs.
In July, the EC raised its renewable energy target from 32% to 40% as part of a wider package of measures designed to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions in the EU by at least 55% by 2030 compared with 1990 levels. The "Fit for 55" package includes more ambitious energy efficiency targets, tighter market rules for the carbon emissions trading scheme (ETS) and a carbon levy on the import of goods from countries with lower costs due to less strict emission standards. To become law, the measures must be agreed by EU countries and the European Parliament.
The EC's directive also set out specific renewable energy targets for the transport, heating and cooling, building and industrial sectors.
Under its Green Deal plan, the EC has pledged to spend one third of the 1.8 trillion euro ($2.1 trillion) investments from the NextGenerationEU covid recovery plan towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Reuters Events