US expands solar farm database; Low power prices threaten projects in Spain
The solar news you need to know.

Related Articles
US expands solar project database to aid developers
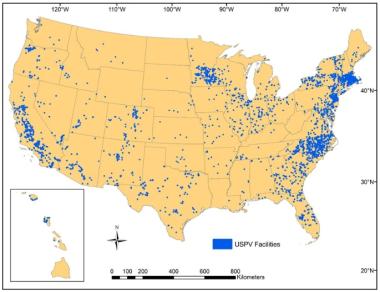
The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has released more data on 3,699 ground-mounted solar facilities across 47 states in an expanded version of the United States Large-Scale Solar Photovoltaic Database (USPVDB).
The collaboration between Berkeley Lab and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) is the "most detailed and comprehensive publicly available large-scale solar facility database to date," Berkeley Lab said in a statement.
Location of solar farms in the US database
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: Berkeley Lab, November 2023
The Biden administration's Inflation Reduction Act has spurred investment in solar and storage projects and created new opportunities for projects in former coal communities and low income areas.
Solar and storage developers can secure 30% investment tax credits (ITCs) and can gain additional tax credit bonuses for projects in areas impacted by the energy transition, designated as low income, or if components are sourced from U.S. factories.
The expanded solar farm database will allow stakeholders to analyse historical trends in utility-scale storage deployment and to "more accurately assess the potential costs and benefits of future development," Berkeley Lab said.
The database includes projects over 1 MW and shows detailed aerial shots of the borders of solar farms.
Data is provided on array area, panel type, axis type, year of installation and rated power capacity. The database also indicates whether the site is being shared with farming through agri-solar arrangements and whether the land was previously contaminated.
Low power prices in Spain threaten solar, wind build
Investments in Spanish renewable energy projects could drop as early as next year if measures are not put in place to mitigate the impact of rising solar and wind capacity on wholesale power prices, national renewable energy association APPA warned on November 6, Reuters reported.
Spain raised its solar and wind targets earlier this year in a draft climate strategy that aims to generate 81% of the country's electricity from renewables by 2030.
Published in June, the strategy doubles the solar target from 39 GW to 76 GW and sets a wind power target of 62 GW by the end of the decade, up from a previous 50 GW target.
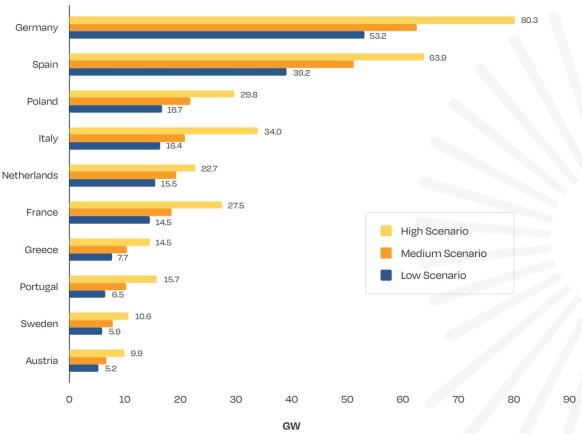
Forecast largest solar markets in the EU in 2023-26
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: SolarPower Europe, December 2022
Rising renewable energy capacity is dampening wholesale power prices during peak resource periods, curbing the returns available to investors.
"If we don't correct that, investments will slow down or disappear," Jose Maria Gonzalez Moya, director general of APPA, told reporters at a presentation.
A significant expansion of energy storage is needed to reduce the impact on prices, he said.
Spain's draft climate strategy set a slightly higher storage target of 22 GW by 2030 but tripled the target for electrolysers to produce green hydrogen to 11 GW.
Spain estimates that it will need investments of 294 billion euros ($322 billion) to hit these targets.
Renewable energy groups have also called on Spain to accelerate grid expansions to curb curtailment risks and reignite power demand by accelerating the rollout of electric vehicles.
EU to award 1.7 billion euros to agri-solar in Italy
The European Union will award 1.7 billion euros ($1.8 billion) to developers of agri-solar projects in Italy under a new scheme approved by the European Commission on November 10.
Agri-solar projects integrate solar farms on working farmland, helping to optimise land resources.
The EU funding will support the deployment of 1 GW of solar capacity under a scheme that will run until the end of 2024.
Developers will be offered investment grants equivalent to 40% of costs and 20-year contract for differences (CFDs) that ensure operators receive a fixed level of income.
Earlier this year, Germany committed to more solar capacity on working farmland as it chases a target of 215 GW of solar by 2030, compared with 63 GW in 2022.
UK to remove projects blocking grid queues
The UK National Grid electricity system operator will remove stalled power generation projects from grid connection queues under a new process that will be launched on November 27, national energy regulator Ofgem said in a statement.
National Grid ESO will terminate stalled projects that are blocking connection queues for high-voltage transmission lines so that projects that are ready to go can be fast-tracked, Ofgem said.
Across Europe and the U.S., solar and wind projects have to wait several years for grid connections as approval authorities work through a high volume of applications.
The new UK rules will apply to existing and future grid connection agreements and the first terminations are "likely to happen as early as 2024," the regulator said.
Last week, National Grid said it will speed up the connection of 10 GW of battery storage on the UK transmission network by around four years and accelerate the connection of 10 GW of solar, wind and storage capacity on the distribution network.
On the transmission network, 19 battery storage projects in England and Wales will be offered connection dates four years earlier than current agreements, on average, by delaying some non-essential engineering works until after connection.
In the Midlands and South West of England and in South Wales, 10 GW of low carbon energy projects will be accelerated with some "shovel ready" projects brought forward by up to five years, National Grid said.
The UK aims to quadruple offshore wind capacity to 50 GW by 2030 and fully decarbonise its power sector by 2035, requiring huge investment in onshore and offshore infrastructure and faster deployment of energy storage.
The announcement by National Grid follows months of engagement with industry, government and Ofgem.
The grid operator has "already been in contact with more than 200 projects interested in fast tracking their distribution connection dates in the first wave of the capacity release, with 16 expressing an interest in connecting in the next 12 months and another 180 looking to connect within two to five years," it said.
A further tranche of clean energy projects, primarily batteries or batteries coupled with wind or solar, will be offered accelerated transmission connections early next year, which could bring forward another 10 GW, National Grid said.
Reuters Events